
All You Need To Know About Ransomware-as-a-Service
We all know the that ransomware is one of the most popular threats on organizations worldwide. It’s results can be devastating in some cases for companies, whether if it is by halting production line that can result with millions lost, causing cancellation of flights by targeting airports, causing a severe damage to a brand reputation by stealing and leaking customers’ information and the list goes on and on.
Behind this industry there is one particular business model that allows the growth and emerging on new threat group constantly – Ransomware-as-a-Service.
This model became so popular and profitable for threat actors, that almost every ransomware group these days apply it.
It does have its pros and cons for the ransomware groups, but overall it seems like the golden egg cyber criminals were looking for.
What Is Ransomware?
Well, as you probably already know, ransomware is simple act of encrypting a persons, or an organization’s, data and demanding ransom for the decryption key.
Over the past years, as defense and backup mechanisms evolved, a new extortion method emerged named “double-extortion” which is demanding ransom not only for the decryption key, but also for not leaking the stollen information.
Given that ransomware group encountered hard negotiations with companies that were able to recover the encrypted data by the various defense services, the decided to add the element of stollen data to their campaigns.
In addition of encrypting the data, they also stealing it. Sure it made them work a little bit harder but overall it put them into a better position and provided a massive leverage in the negotiation with their victims.
For example, let’s say an energy company were compromised and all of their secret projects and patents were stolen. Even if their recovery services work, their main risk here is that all of this information will leak outside and it can cause severe damage to the company that maybe won’t be able to recover from this.
What is Ransomware-as-a-Service?
So now that we understand what is ransomware, the remained questions are: but how these groups operated? are we talking about a small group that does it all? who are the developers? who are the hackers? who does the negotiations?
This is exactly the order in the chaos RaaS provides.
Ransomware-as-a-Service is a unique business model that provides flexibility and efficiency for threat actors – Instead of doing it all, everyone does exactly what they are specialize in, and everyone gets their cut.
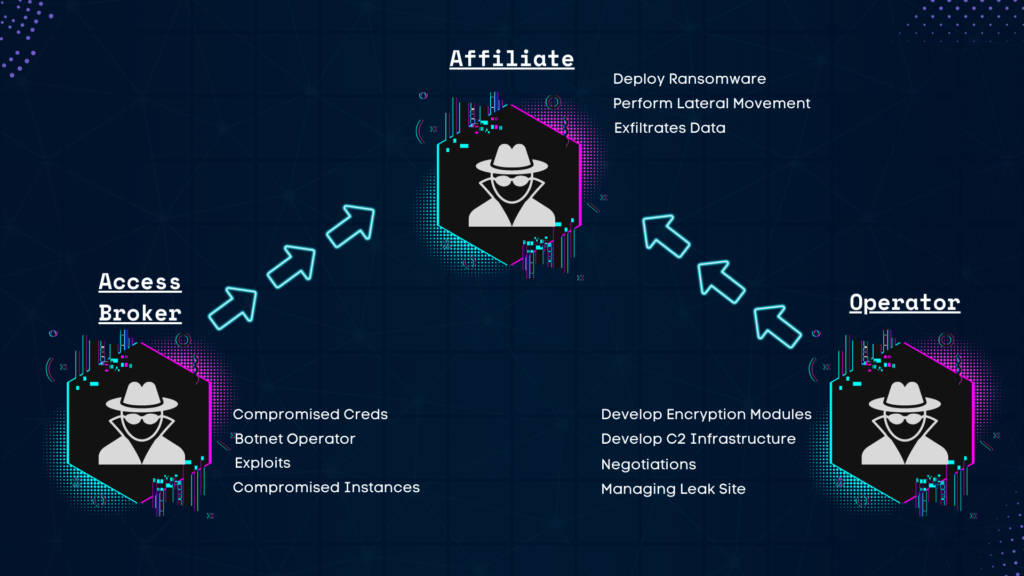
RaaS process of operation is divided in three different pillars – Operators, Affiliates, and Access Brokers.
Operators
The operators or the ones we mostly see behind any RaaS operation, the founders of the group.
Their main role within the ransomware organization is to develop and maintain the infrastructures, the tools and encryptors the eventually the affiliates will use.
They are the developers of the product and their responsibility is to do their tools as fast and as efficient and lethal as possible.
Few examples of what operators will do is to write the code that will encrypt the files within the victim’s machine, utilize vulnerabilities on various operation systems the group targets, provide lateral movement tools and create the C2 infrastructure in matters of anonymity and as less suspicious as possible.
In addition, the operators are the ones who run the operation, ie. the ones that other threat actors should talk to if they want to join, they are the ones who are in charge of the finance, money laundering, PR, negotiation with victims, and other managerial and strategic roles.
Affiliates
Affiliates are the ones who does the dirty work most of the times.
A RaaS business model can not exist without talented affiliates that will be the ones who infiltrate the victim’s network and deploy the ransomware the operators created.
The relationship between the operators and affiliates is that the affiliates eventually use the operators products.
An affiliate is most of the times is not bound to any ransomware group and they can team up with any ransomware organization they want. Although i do believe that eventually if they are being rewarded enough and the product is good, they don’t have a real reason to go with other ransomware organizations.
The affiliates can be considered as the red teamers, given the fact that they have knowledge of how to deploy ransomware and they have good knowledge about organizations’ security infrastructure, lateral movement, assets scanning, bypassing defense mechanisms, and more.
When it comes to the payment, the affiliates will get a cut of the ransom depending on that the operators were able to get from the victim – Mostly a percentage of the ransom.
Access Brokers
Although Access brokers give their services to many types of threat actors and not only to ransomware groups, access brokers play a crucial part in the work affiliates often do.
Although an affiliate can be a very talented individual that has his/her own hacking techniques, it is often way easier use contractors and other types of services threat actors mostly offer.
Access broker can be someone who sells access to an organization in a form of compromised credentials, hacked RDP instances, zero-day exploits for certain technologies and more.
The most interesting service access brokers sell to affiliates are botnets access.
One of the most common examples we know is the relationship between Conti’s affiliates and Trickbot. The affiliates used to buy access to Trickbot’s infected machines of organizations worldwide and with that access all that is left to do is deploy the ransomware modules Conti developed. Although Conti is not active anymore, Trickbot is still an active threat in our lives.
The relationship between Botnets’ operators and ransomware affiliates is pretty popular these days. Another more recent case was BlackBasta’s affiliate that used Qakbot as a initial access method to organizations and used it to deploy the BlackBasta’s payload.
As mentioned, affiliates can be a very talented access brokers but having the ability to pay and have access in an instant make their lives much easier.
The relationship between access brokers and ransomware groups are not new, but also very natural and in some cases there are some speculations that ransomware groups operators offer exclusive partnerships with certain botnets.
The overall business module map looks like so:
Conclusions
As we know understand it better, we can see that RaaS is a business model that help threat group and ransomware operators to make the best of the abilities for each phase of their campaigns.
They were able to develop a mechanism that get’s them maximum results with minimum hassle as they can focus only on developing their product and give the rest of the work to other individuals that are specialized in compromising networks and obtaining initial access.
The reason behind the success of the ransomware industry despite the advancements of security products is mainly because these days ransomware group can go by the tens and even hundreds of people given this business module.
